Understanding Water Diseases: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
Water is an essential component of life, but it can also be a source of danger when contaminated. Water diseases pose a significant threat to public health globally. In this 2000-word article, we will delve into the world of water diseases, exploring their causes, effects, prevention, and treatment.
What Are Water Diseases?
Defining the Threat
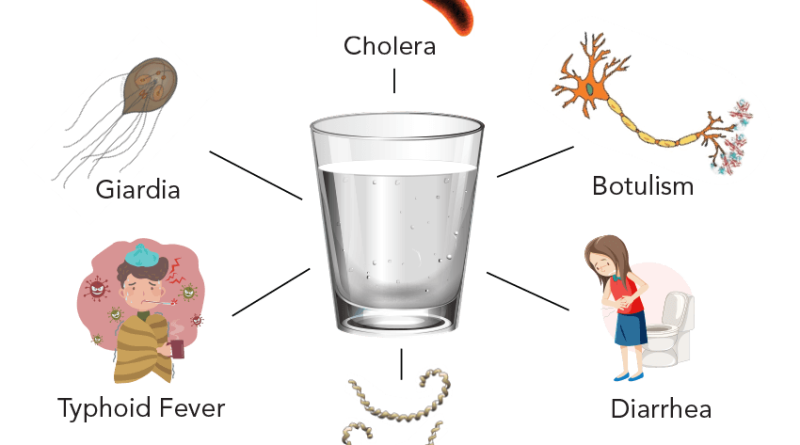
Water diseases, as the name suggests, are illnesses that are transmitted through contaminated water sources. These diseases can affect anyone, irrespective of age or gender. They are caused by various pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, and parasites, which contaminate water bodies such as lakes, rivers, and even tap water.
Common Water Diseases
-
Cholera
Cholera is a highly contagious bacterial infection caused by Vibrio cholerae. It spreads through the consumption of contaminated water or food. Symptoms include severe diarrhea, vomiting, and dehydration, which can lead to death if not treated promptly.
-
Giardiasis
Giardiasis is caused by the parasite Giardia lamblia. It is commonly contracted by ingesting water contaminated with fecal matter. Symptoms include diarrhea, abdominal cramps, and nausea.
-
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A is a viral infection that affects the liver. It can be transmitted through water contaminated with the feces of an infected person. Symptoms include jaundice, fatigue, and abdominal pain.
-
Dysentery
Dysentery is a bacterial or parasitic infection that leads to severe diarrhea with blood. Contaminated water is a common source of this disease. Symptoms include abdominal pain and frequent, bloody stools.
Causes of Water Contamination
-
Sewage and Waste Disposal
Improper sewage disposal and waste management can lead to the contamination of water sources. When sewage systems are poorly maintained, pathogens can enter the water supply, causing diseases.
-
Agricultural Runoff
Pesticides and fertilizers used in agriculture can seep into groundwater and surface water, contaminating them with harmful chemicals and pathogens.
-
Industrial Pollution
Industrial discharge often contains toxic substances that can contaminate nearby water bodies. This pollution can have severe health consequences for those who rely on these water sources.
The Impact of Water Diseases
Health Consequences
Water diseases can have devastating effects on human health. They can lead to severe dehydration, malnutrition, and even death, especially in children and the elderly.
Economic Burden
The treatment and management of water diseases place a significant economic burden on healthcare systems and affected individuals. Lost productivity due to illness also impacts economies.
Prevention and Treatment
-
Water Treatment
Ensuring access to clean and safe drinking water is crucial in preventing water diseases. Filtration and purification methods can remove contaminants and pathogens.
-
Sanitation
Improved sanitation practices, including proper waste disposal and sewage management, can prevent the contamination of water sources.
-
Vaccination
Vaccination against diseases like hepatitis A can provide long-term protection and reduce the risk of infection.
-
Hygiene Education
Educating communities about proper hygiene practices, such as handwashing, can significantly reduce the transmission of water borne diseases.
Conclusion
In conclusion, water borne diseases are a serious global health concern that affects millions of people each year. Understanding the causes, effects, prevention, and treatment of these diseases is essential in combating this threat. Access to clean and safe water, improved sanitation, and education are key factors in reducing the prevalence of water borne diseases.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
- How can I ensure the safety of my drinking water at home?
To ensure the safety of your drinking water, you can install a water filtration system or boil water before consumption. Regularly maintain your water sources and storage containers.
- Are waterborne diseases more prevalent in certain regions?
Yes, waterborne diseases are more common in regions with poor sanitation and limited access to clean water. Developing countries often face higher risks.
- Can waterborne diseases be fatal?
Yes, some waterborne diseases, like cholera, can be fatal if not treated promptly. Dehydration is a common complication.
- What role does government play in preventing waterborne diseases?
Governments play a vital role in implementing water quality standards, providing clean water infrastructure, and promoting public awareness campaigns to prevent waterborne diseases.
- How can I contribute to the prevention of waterborne diseases?
You can contribute by supporting organizations that work to improve water and sanitation conditions in vulnerable communities, practicing good hygiene, and spreading awareness about waterborne diseases.
Also, Read about: Understanding Blood Diseases: A Comprehensive Guide